Connecting to Databases
Superset does not ship bundled with connectivity to databases. The main step in connecting Superset to a database is to install the proper database driver(s) in your environment.
You’ll need to install the required packages for the database you want to use as your metadata database as well as the packages needed to connect to the databases you want to access through Superset. For information about setting up Superset's metadata database, please refer to installation documentations (Docker Compose, Kubernetes)
This documentation tries to keep pointer to the different drivers for commonly used database engine.
Installing Database Drivers
Superset requires a Python DB-API database driver and a SQLAlchemy dialect to be installed for each database engine you want to connect to.
You can read more here about how to install new database drivers into your Superset configuration.
Supported Databases and Dependencies
Some of the recommended packages are shown below. Please refer to pyproject.toml for the versions that are compatible with Superset.
Database | PyPI package | Connection String |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Athena | pip install pyathena[pandas] , pip install PyAthenaJDBC | awsathena+rest://{access_key_id}:{access_key}@athena.{region}.amazonaws.com/{schema}?s3_staging_dir={s3_staging_dir}&... |
| AWS DynamoDB | pip install pydynamodb | dynamodb://{access_key_id}:{secret_access_key}@dynamodb.{region_name}.amazonaws.com?connector=superset |
| AWS Redshift | pip install sqlalchemy-redshift | redshift+psycopg2://<userName>:<DBPassword>@<AWS End Point>:5439/<Database Name> |
| Apache Doris | pip install pydoris | doris://<User>:<Password>@<Host>:<Port>/<Catalog>.<Database> |
| Apache Drill | pip install sqlalchemy-drill | drill+sadrill://<username>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<storage_plugin>, often useful: ?use_ssl=True/False |
| Apache Druid | pip install pydruid | druid://<User>:<password>@<Host>:<Port-default-9088>/druid/v2/sql |
| Apache Hive | pip install pyhive | hive://hive@{hostname}:{port}/{database} |
| Apache Impala | pip install impyla | impala://{hostname}:{port}/{database} |
| Apache Kylin | pip install kylinpy | kylin://<username>:<password>@<hostname>:<port>/<project>?<param1>=<value1>&<param2>=<value2> |
| Apache Pinot | pip install pinotdb | pinot://BROKER:5436/query?server=http://CONTROLLER:5983/ |
| Apache Solr | pip install sqlalchemy-solr | solr://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{server_path}/{collection} |
| Apache Spark SQL | pip install pyhive | hive://hive@{hostname}:{port}/{database} |
| Arc - Apache Arrow | pip install arc-superset-arrow | arc+arrow://{api_key}@{hostname}:{port}/{database} |
| Arc - JSON | pip install arc-superset-dialect | arc+json://{api_key}@{hostname}:{port}/{database} |
| Ascend.io | pip install impyla | ascend://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}?auth_mechanism=PLAIN;use_ssl=true |
| Azure MS SQL | pip install pymssql | mssql+pymssql://UserName@presetSQL:TestPassword@presetSQL.database.windows.net:1433/TestSchema |
| ClickHouse | pip install clickhouse-connect | clickhousedb://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database} |
| Cloudflare D1 | pip install superset-engine-d1 or pip install apache_superset[d1] | d1://{cloudflare_account_id}:{cloudflare_api_token}@{cloudflare_d1_database_id} |
| CockroachDB | pip install cockroachdb | cockroachdb://root@{hostname}:{port}/{database}?sslmode=disable |
| Couchbase | pip install couchbase-sqlalchemy | couchbase://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}?truststorepath={ssl certificate path} |
| CrateDB | pip install sqlalchemy-cratedb | crate://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}, often useful: ?ssl=true/false or ?schema=testdrive. |
| Denodo | pip install denodo-sqlalchemy | denodo://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database} |
| Dremio | pip install sqlalchemy_dremio | dremio+flight://{username}:{password}@{host}:32010, often useful: ?UseEncryption=true/false. For Legacy ODBC: dremio+pyodbc://{username}:{password}@{host}:31010 |
| Elasticsearch | pip install elasticsearch-dbapi | elasticsearch+http://{user}:{password}@{host}:9200/ |
| Exasol | pip install sqlalchemy-exasol | exa+pyodbc://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/my_schema?CONNECTIONLCALL=en_US.UTF-8&driver=EXAODBC |
| Google BigQuery | pip install sqlalchemy-bigquery | bigquery://{project_id} |
| Google Sheets | pip install shillelagh[gsheetsapi] | gsheets:// |
| Firebolt | pip install firebolt-sqlalchemy | firebolt://{client_id}:{client_secret}@{database}/{engine_name}?account_name={name} |
| Hologres | pip install psycopg2 | postgresql+psycopg2://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>/<Database Name> |
| IBM Db2 | pip install ibm_db_sa | db2+ibm_db:// |
| IBM Netezza Performance Server | pip install nzalchemy | netezza+nzpy://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>/<Database Name> |
| MySQL | pip install mysqlclient | mysql://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>/<Database Name> |
| OceanBase | pip install oceanbase_py | oceanbase://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>/<Database Name> |
| Oracle | pip install oracledb | oracle://<username>:<password>@<hostname>:<port> |
| Parseable | pip install sqlalchemy-parseable | parseable://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>/<Stream Name> |
| PostgreSQL | pip install psycopg2 | postgresql://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>/<Database Name> |
| Presto | pip install pyhive | presto://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database} |
| SAP Hana | pip install hdbcli sqlalchemy-hana or pip install apache_superset[hana] | hana://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port} |
| SingleStore | pip install sqlalchemy-singlestoredb | singlestoredb://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database} |
| StarRocks | pip install starrocks | starrocks://<User>:<Password>@<Host>:<Port>/<Catalog>.<Database> |
| Snowflake | pip install snowflake-sqlalchemy | snowflake://{user}:{password}@{account}.{region}/{database}?role={role}&warehouse={warehouse} |
| SQLite | No additional library needed | sqlite://path/to/file.db?check_same_thread=false |
| SQL Server | pip install pymssql | mssql+pymssql://<Username>:<Password>@<Host>:<Port-default:1433>/<Database Name> |
| TDengine | pip install taospy pip install taos-ws-py | taosws://<user>:<password>@<host>:<port> |
| Teradata | pip install teradatasqlalchemy | teradatasql://{user}:{password}@{host} |
| TimescaleDB | pip install psycopg2 | postgresql://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>:<Port>/<Database Name> |
| Trino | pip install trino | trino://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{catalog} |
| Vertica | pip install sqlalchemy-vertica-python | vertica+vertica_python://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>/<Database Name> |
| YDB | pip install ydb-sqlalchemy | ydb://{host}:{port}/{database_name} |
| YugabyteDB | pip install psycopg2 | postgresql://<UserName>:<DBPassword>@<Database Host>/<Database Name> |
Note that many other databases are supported, the main criteria being the existence of a functional SQLAlchemy dialect and Python driver. Searching for the keyword "sqlalchemy + (database name)" should help get you to the right place.
If your database or data engine isn't on the list but a SQL interface exists, please file an issue on the Superset GitHub repo, so we can work on documenting and supporting it.
Additional Resources
Installing Drivers in Docker Images
Superset requires a Python database driver to be installed for each additional type of database you want to connect to.
In this example, we'll walk through how to install the MySQL connector library. The connector library installation process is the same for all additional libraries.
1. Determine the driver you need
Consult the list of database drivers
and find the PyPI package needed to connect to your database. In this example, we're connecting
to a MySQL database, so we'll need the mysqlclient connector library.
2. Install the driver in the container
We need to get the mysqlclient library installed into the Superset docker container
(it doesn't matter if it's installed on the host machine). We could enter the running
container with docker exec -it <container_name> bash and run pip install mysqlclient
there, but that wouldn't persist permanently.
To address this, the Superset docker compose deployment uses the convention
of a requirements-local.txt file. All packages listed in this file will be installed
into the container from PyPI at runtime. This file will be ignored by Git for
the purposes of local development.
Create the file requirements-local.txt in a subdirectory called docker that
exists in the directory with your docker-compose.yml or docker-compose-non-dev.yml file.
# Run from the repo root:
touch ./docker/requirements-local.txt
Add the driver identified in step above. You can use a text editor or do it from the command line like:
echo "mysqlclient" >> ./docker/requirements-local.txt
If you are running a stock (non-customized) Superset image, you are done.
Launch Superset with docker compose -f docker-compose-non-dev.yml up and
the driver should be present.
You can check its presence by entering the running container with
docker exec -it <container_name> bash and running pip freeze. The PyPI package should
be present in the printed list.
If you're running a customized docker image, rebuild your local image with the new driver baked in:
docker compose build --force-rm
After the rebuild of the Docker images is complete, relaunch Superset by
running docker compose up.
3. Connect to MySQL
Now that you've got a MySQL driver installed in your container, you should be able to connect to your database via the Superset web UI.
As an admin user, go to Settings -> Data: Database Connections and click the +DATABASE button. From there, follow the steps on the Using Database Connection UI page.
Consult the page for your specific database type in the Superset documentation to determine the connection string and any other parameters you need to input. For instance, on the MySQL page, we see that the connection string to a local MySQL database differs depending on whether the setup is running on Linux or Mac.
Click the “Test Connection” button, which should result in a popup message saying, "Connection looks good!".
4. Troubleshooting
If the test fails, review your docker logs for error messages. Superset uses SQLAlchemy to connect to databases; to troubleshoot the connection string for your database, you might start Python in the Superset application container or host environment and try to connect directly to the desired database and fetch data. This eliminates Superset for the purposes of isolating the problem.
Repeat this process for each type of database you want Superset to connect to.
Database-specific Instructions
Ascend.io
The recommended connector library to Ascend.io is impyla.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
ascend://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}?auth_mechanism=PLAIN;use_ssl=true
Apache Doris
The sqlalchemy-doris library is the recommended way to connect to Apache Doris through SQLAlchemy.
You'll need the following setting values to form the connection string:
- User: User Name
- Password: Password
- Host: Doris FE Host
- Port: Doris FE port
- Catalog: Catalog Name
- Database: Database Name
Here's what the connection string looks like:
doris://<User>:<Password>@<Host>:<Port>/<Catalog>.<Database>
Additional Resources
AWS Athena
PyAthenaJDBC
PyAthenaJDBC is a Python DB 2.0 compliant wrapper for the Amazon Athena JDBC driver.
The connection string for Amazon Athena is as follows:
awsathena+jdbc://{aws_access_key_id}:{aws_secret_access_key}@athena.{region_name}.amazonaws.com/{schema_name}?s3_staging_dir={s3_staging_dir}&...
Note that you'll need to escape & encode when forming the connection string like so:
s3://... -> s3%3A//...
PyAthena
You can also use the PyAthena library (no Java required) with the following connection string:
awsathena+rest://{aws_access_key_id}:{aws_secret_access_key}@athena.{region_name}.amazonaws.com/{schema_name}?s3_staging_dir={s3_staging_dir}&...
The PyAthena library also allows to assume a specific IAM role which you can define by adding following parameters in Superset's Athena database connection UI under ADVANCED --> Other --> ENGINE PARAMETERS.
{
"connect_args": {
"role_arn": "<role arn>"
}
}
AWS DynamoDB
PyDynamoDB
PyDynamoDB is a Python DB API 2.0 (PEP 249) client for Amazon DynamoDB.
The connection string for Amazon DynamoDB is as follows:
dynamodb://{aws_access_key_id}:{aws_secret_access_key}@dynamodb.{region_name}.amazonaws.com:443?connector=superset
To get more documentation, please visit: PyDynamoDB WIKI.
AWS Redshift
The sqlalchemy-redshift library is the recommended way to connect to Redshift through SQLAlchemy.
This dialect requires either redshift_connector or psycopg2 to work properly.
You'll need to set the following values to form the connection string:
- User Name: userName
- Password: DBPassword
- Database Host: AWS Endpoint
- Database Name: Database Name
- Port: default 5439
psycopg2
Here's what the SQLALCHEMY URI looks like:
redshift+psycopg2://<userName>:<DBPassword>@<AWS End Point>:5439/<Database Name>
redshift_connector
Here's what the SQLALCHEMY URI looks like:
redshift+redshift_connector://<userName>:<DBPassword>@<AWS End Point>:5439/<Database Name>
Using IAM-based credentials with Redshift cluster
Amazon redshift cluster also supports generating temporary IAM-based database user credentials.
Your superset app's IAM role should have permissions to call the redshift:GetClusterCredentials operation.
You have to define the following arguments in Superset's redshift database connection UI under ADVANCED --> Others --> ENGINE PARAMETERS.
{"connect_args":{"iam":true,"database":"<database>","cluster_identifier":"<cluster_identifier>","db_user":"<db_user>"}}
and SQLALCHEMY URI should be set to redshift+redshift_connector://
Using IAM-based credentials with Redshift serverless
Redshift serverless supports connection using IAM roles.
Your superset app's IAM role should have redshift-serverless:GetCredentials and redshift-serverless:GetWorkgroup permissions on Redshift serverless workgroup.
You have to define the following arguments in Superset's redshift database connection UI under ADVANCED --> Others --> ENGINE PARAMETERS.
{"connect_args":{"iam":true,"is_serverless":true,"serverless_acct_id":"<aws account number>","serverless_work_group":"<redshift work group>","database":"<database>","user":"IAMR:<superset iam role name>"}}
ClickHouse
To use ClickHouse with Superset, you will need to install the clickhouse-connect Python library:
If running Superset using Docker Compose, add the following to your ./docker/requirements-local.txt file:
clickhouse-connect>=0.6.8
The recommended connector library for ClickHouse is clickhouse-connect.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
clickhousedb://<user>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<database>[?options…]clickhouse://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
Here's a concrete example of a real connection string:
clickhousedb://demo:demo@github.demo.trial.altinity.cloud/default?secure=true
If you're using Clickhouse locally on your computer, you can get away with using a http protocol URL that uses the default user without a password (and doesn't encrypt the connection):
clickhousedb://localhost/default
Additional Resources
Cloudflare D1
To use Cloudflare D1 with superset, install the superset-engine-d1 library.
pip install superset-engine-d1
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
d1://{cloudflare_account_id}:{cloudflare_api_token}@{cloudflare_d1_database_id}
CockroachDB
The recommended connector library for CockroachDB is sqlalchemy-cockroachdb.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
cockroachdb://root@{hostname}:{port}/{database}?sslmode=disable
Couchbase
The Couchbase's Superset connection is designed to support two services: Couchbase Analytics and Couchbase Columnar. The recommended connector library for couchbase is couchbase-sqlalchemy.
pip install couchbase-sqlalchemy
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
couchbase://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}?truststorepath={certificate path}?ssl={true/false}
CrateDB
The connector library for CrateDB is sqlalchemy-cratedb.
We recommend to add the following item to your requirements.txt file:
sqlalchemy-cratedb>=0.40.1,<1
An SQLAlchemy connection string for CrateDB Self-Managed on localhost, for evaluation purposes, looks like this:
crate://crate@127.0.0.1:4200
An SQLAlchemy connection string for connecting to CrateDB Cloud looks like this:
crate://<username>:<password>@<clustername>.cratedb.net:4200/?ssl=true
Follow the steps here to install the CrateDB connector package when setting up Superset locally using Docker Compose.
echo "sqlalchemy-cratedb" >> ./docker/requirements-local.txt
Additional Resources
Databend
The recommended connector library for Databend is databend-sqlalchemy.
Superset has been tested on databend-sqlalchemy>=0.2.3.
The recommended connection string is:
databend://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database_name}
Here's a connection string example of Superset connecting to a Databend database:
databend://user:password@localhost:8000/default?secure=false
Databricks
Databricks now offer a native DB API 2.0 driver, databricks-sql-connector, that can be used with the sqlalchemy-databricks dialect. You can install both with:
pip install "apache-superset[databricks]"
To use the Hive connector you need the following information from your cluster:
- Server hostname
- Port
- HTTP path
These can be found under "Configuration" -> "Advanced Options" -> "JDBC/ODBC".
You also need an access token from "Settings" -> "User Settings" -> "Access Tokens".
Once you have all this information, add a database of type "Databricks Native Connector" and use the following SQLAlchemy URI:
databricks+connector://token:{access_token}@{server_hostname}:{port}/{database_name}
You also need to add the following configuration to "Other" -> "Engine Parameters", with your HTTP path:
{
"connect_args": {"http_path": "sql/protocolv1/o/****"}
}
Older driver
Originally Superset used databricks-dbapi to connect to Databricks. You might want to try it if you're having problems with the official Databricks connector:
pip install "databricks-dbapi[sqlalchemy]"
There are two ways to connect to Databricks when using databricks-dbapi: using a Hive connector or an ODBC connector. Both ways work similarly, but only ODBC can be used to connect to SQL endpoints.
Hive
To connect to a Hive cluster add a database of type "Databricks Interactive Cluster" in Superset, and use the following SQLAlchemy URI:
databricks+pyhive://token:{access_token}@{server_hostname}:{port}/{database_name}
You also need to add the following configuration to "Other" -> "Engine Parameters", with your HTTP path:
{"connect_args": {"http_path": "sql/protocolv1/o/****"}}
ODBC
For ODBC you first need to install the ODBC drivers for your platform.
For a regular connection use this as the SQLAlchemy URI after selecting either "Databricks Interactive Cluster" or "Databricks SQL Endpoint" for the database, depending on your use case:
databricks+pyodbc://token:{access_token}@{server_hostname}:{port}/{database_name}
And for the connection arguments:
{"connect_args": {"http_path": "sql/protocolv1/o/****", "driver_path": "/path/to/odbc/driver"}}
The driver path should be:
/Library/simba/spark/lib/libsparkodbc_sbu.dylib(Mac OS)/opt/simba/spark/lib/64/libsparkodbc_sb64.so(Linux)
For a connection to a SQL endpoint you need to use the HTTP path from the endpoint:
{"connect_args": {"http_path": "/sql/1.0/endpoints/****", "driver_path": "/path/to/odbc/driver"}}
Denodo
The recommended connector library for Denodo is denodo-sqlalchemy.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows (default port is 9996):
denodo://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
Dremio
The recommended connector library for Dremio is sqlalchemy_dremio.
The expected connection string for ODBC (Default port is 31010) is formatted as follows:
dremio+pyodbc://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database_name}/dremio?SSL=1
The expected connection string for Arrow Flight (Dremio 4.9.1+. Default port is 32010) is formatted as follows:
dremio+flight://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/dremio
Additional Resources
Apache Drill
SQLAlchemy
The recommended way to connect to Apache Drill is through SQLAlchemy. You can use the sqlalchemy-drill package.
Once that is done, you can connect to Drill in two ways, either via the REST interface or by JDBC. If you are connecting via JDBC, you must have the Drill JDBC Driver installed.
The basic connection string for Drill looks like this:
drill+sadrill://<username>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<storage_plugin>?use_ssl=True
To connect to Drill running on a local machine running in embedded mode you can use the following connection string:
drill+sadrill://localhost:8047/dfs?use_ssl=False
JDBC
Connecting to Drill through JDBC is more complicated and we recommend following this tutorial.
The connection string looks like:
drill+jdbc://<username>:<password>@<host>:<port>
ODBC
We recommend reading the Apache Drill documentation and read the GitHub README to learn how to work with Drill through ODBC.
Additional Resources
Apache Druid
A native connector to Druid ships with Superset (behind the DRUID_IS_ACTIVE flag) but this is
slowly getting deprecated in favor of the SQLAlchemy / DBAPI connector made available in the
pydruid library.
The connection string looks like:
druid://<User>:<password>@<Host>:<Port-default-9088>/druid/v2/sql
Here's a breakdown of the key components of this connection string:
User: username portion of the credentials needed to connect to your databasePassword: password portion of the credentials needed to connect to your databaseHost: IP address (or URL) of the host machine that's running your databasePort: specific port that's exposed on your host machine where your database is running
Customizing Druid Connection
When adding a connection to Druid, you can customize the connection a few different ways in the Add Database form.
Custom Certificate
You can add certificates in the Root Certificate field when configuring the new database connection to Druid:
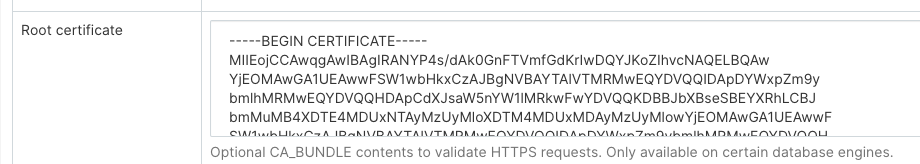
When using a custom certificate, pydruid will automatically use https scheme.
Disable SSL Verification
To disable SSL verification, add the following to the Extras field:
engine_params:
{"connect_args":
{"scheme": "https", "ssl_verify_cert": false}}
Aggregations
Common aggregations or Druid metrics can be defined and used in Superset. The first and simpler use case is to use the checkbox matrix exposed in your datasource’s edit view (Sources -> Druid Datasources -> [your datasource] -> Edit -> [tab] List Druid Column).
Clicking the GroupBy and Filterable checkboxes will make the column appear in the related dropdowns while in the Explore view. Checking Count Distinct, Min, Max or Sum will result in creating new metrics that will appear in the List Druid Metric tab upon saving the datasource.
By editing these metrics, you’ll notice that their JSON element corresponds to Druid aggregation definition. You can create your own aggregations manually from the List Druid Metric tab following Druid documentation.
Post-Aggregations
Druid supports post aggregation and this works in Superset. All you have to do is create a metric,
much like you would create an aggregation manually, but specify postagg as a Metric Type. You
then have to provide a valid json post-aggregation definition (as specified in the Druid docs) in
the JSON field.
Additional Resources
Elasticsearch
The recommended connector library for Elasticsearch is elasticsearch-dbapi.
The connection string for Elasticsearch looks like this:
elasticsearch+http://{user}:{password}@{host}:9200/
Using HTTPS
elasticsearch+https://{user}:{password}@{host}:9200/
Elasticsearch as a default limit of 10000 rows, so you can increase this limit on your cluster or set Superset’s row limit on config
ROW_LIMIT = 10000
You can query multiple indices on SQL Lab for example
SELECT timestamp, agent FROM "logstash"
But, to use visualizations for multiple indices you need to create an alias index on your cluster
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "add" : { "index" : "logstash-**", "alias" : "logstash_all" } }
]
}
Then register your table with the alias name logstash_all
Time zone
By default, Superset uses UTC time zone for elasticsearch query. If you need to specify a time zone, please edit your Database and enter the settings of your specified time zone in the Other > ENGINE PARAMETERS:
{
"connect_args": {
"time_zone": "Asia/Shanghai"
}
}
Another issue to note about the time zone problem is that before elasticsearch7.8, if you want to convert a string into a DATETIME object,
you need to use the CAST function,but this function does not support our time_zone setting. So it is recommended to upgrade to the version after elasticsearch7.8.
After elasticsearch7.8, you can use the DATETIME_PARSE function to solve this problem.
The DATETIME_PARSE function is to support our time_zone setting, and here you need to fill in your elasticsearch version number in the Other > VERSION setting.
the superset will use the DATETIME_PARSE function for conversion.
Disable SSL Verification
To disable SSL verification, add the following to the SQLALCHEMY URI field:
elasticsearch+https://{user}:{password}@{host}:9200/?verify_certs=False
Additional Resources
Exasol
The recommended connector library for Exasol is sqlalchemy-exasol.
The connection string for Exasol looks like this:
exa+pyodbc://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/my_schema?CONNECTIONLCALL=en_US.UTF-8&driver=EXAODBC
Firebird
The recommended connector library for Firebird is sqlalchemy-firebird.
Superset has been tested on sqlalchemy-firebird>=0.7.0, <0.8.
The recommended connection string is:
firebird+fdb://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}//{path_to_db_file}
Here's a connection string example of Superset connecting to a local Firebird database:
firebird+fdb://SYSDBA:masterkey@192.168.86.38:3050//Library/Frameworks/Firebird.framework/Versions/A/Resources/examples/empbuild/employee.fdb
Firebolt
The recommended connector library for Firebolt is firebolt-sqlalchemy.
The recommended connection string is:
firebolt://{username}:{password}@{database}?account_name={name}
or
firebolt://{username}:{password}@{database}/{engine_name}?account_name={name}
It's also possible to connect using a service account:
firebolt://{client_id}:{client_secret}@{database}?account_name={name}
or
firebolt://{client_id}:{client_secret}@{database}/{engine_name}?account_name={name}
Additional Resources
Google BigQuery
The recommended connector library for BigQuery is sqlalchemy-bigquery.
Install BigQuery Driver
Follow the steps here about how to install new database drivers when setting up Superset locally via docker compose.
echo "sqlalchemy-bigquery" >> ./docker/requirements-local.txt
Connecting to BigQuery
When adding a new BigQuery connection in Superset, you'll need to add the GCP Service Account credentials file (as a JSON).
- Create your Service Account via the Google Cloud Platform control panel, provide it access to the appropriate BigQuery datasets, and download the JSON configuration file for the service account.
- In Superset, you can either upload that JSON or add the JSON blob in the following format (this should be the content of your credential JSON file):
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "...",
"private_key_id": "...",
"private_key": "...",
"client_email": "...",
"client_id": "...",
"auth_uri": "...",
"token_uri": "...",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "...",
"client_x509_cert_url": "..."
}
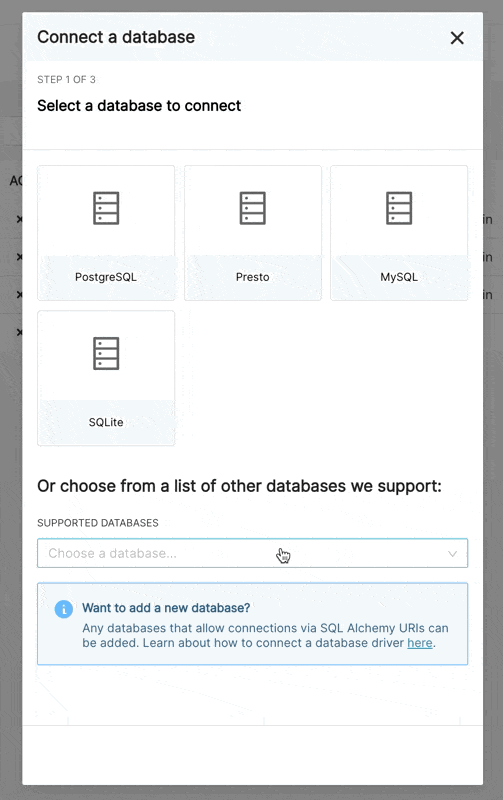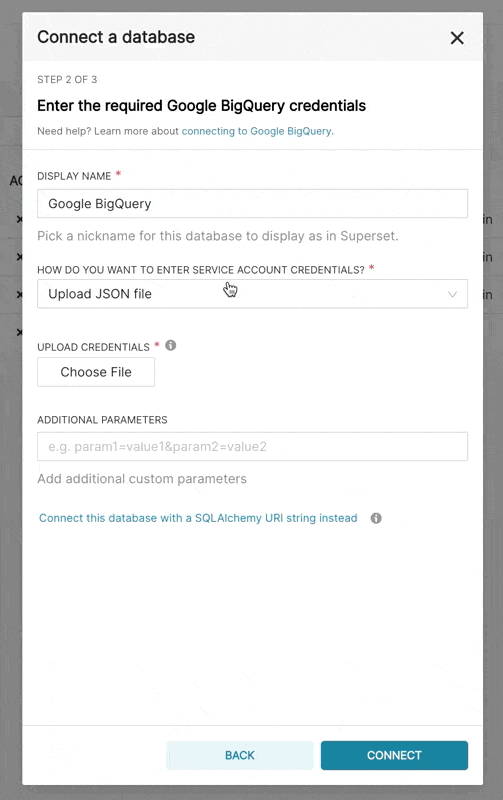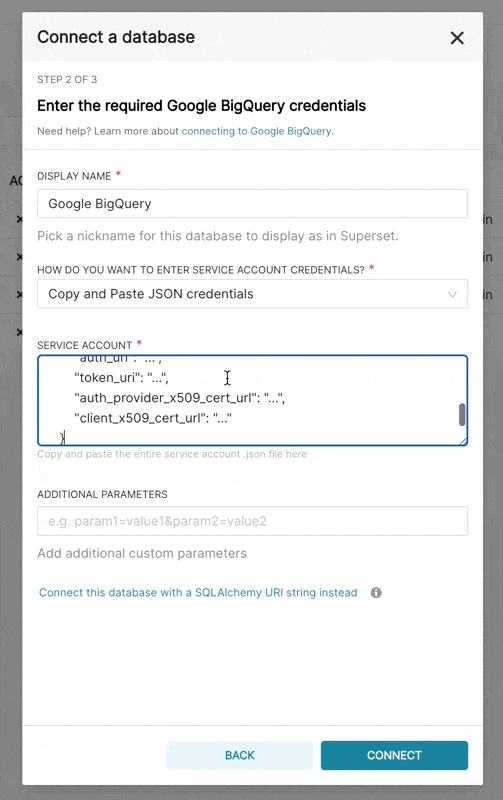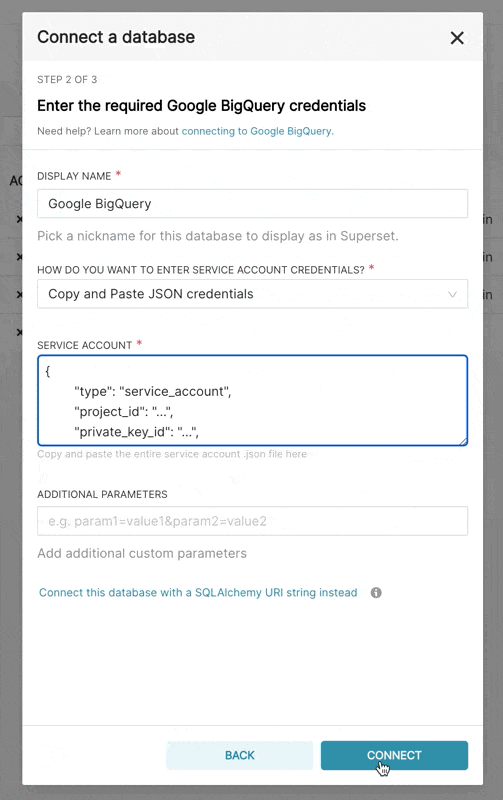
-
Additionally, can connect via SQLAlchemy URI instead
The connection string for BigQuery looks like:
bigquery://{project_id}Go to the Advanced tab, Add a JSON blob to the Secure Extra field in the database configuration form with the following format:
{
"credentials_info": <contents of credentials JSON file>
}The resulting file should have this structure:
{
"credentials_info": {
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "...",
"private_key_id": "...",
"private_key": "...",
"client_email": "...",
"client_id": "...",
"auth_uri": "...",
"token_uri": "...",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "...",
"client_x509_cert_url": "..."
}
}
You should then be able to connect to your BigQuery datasets.
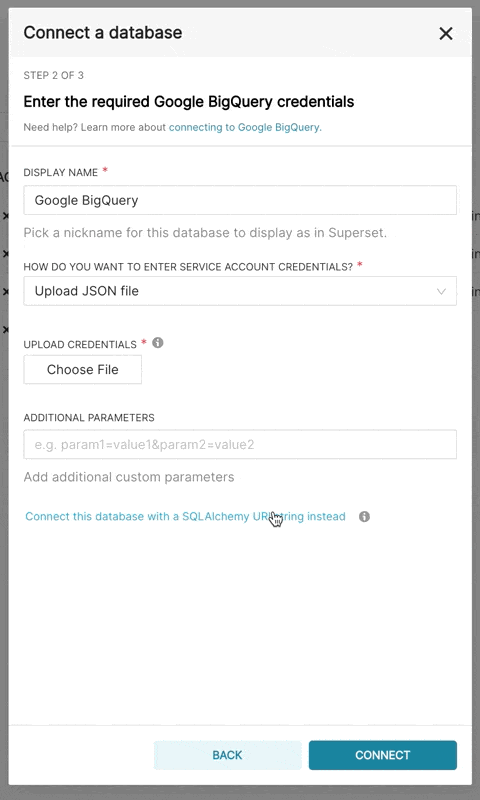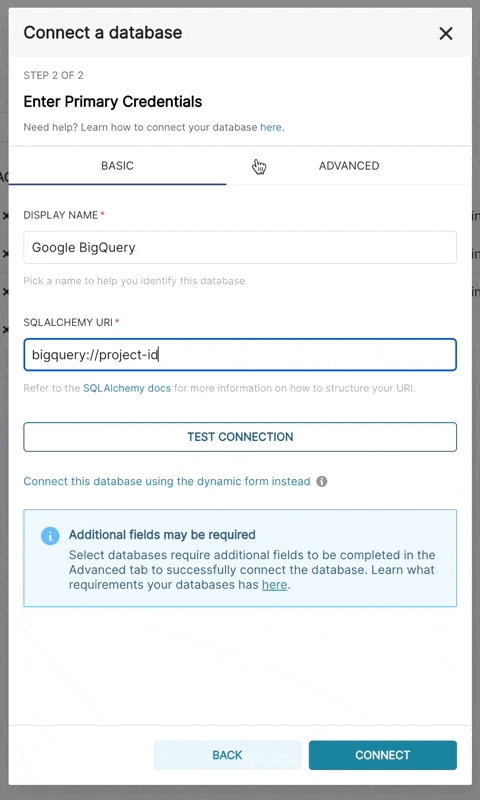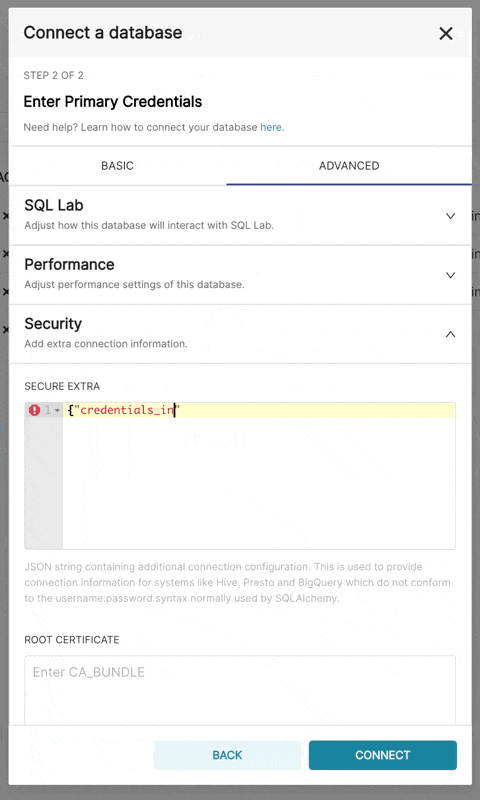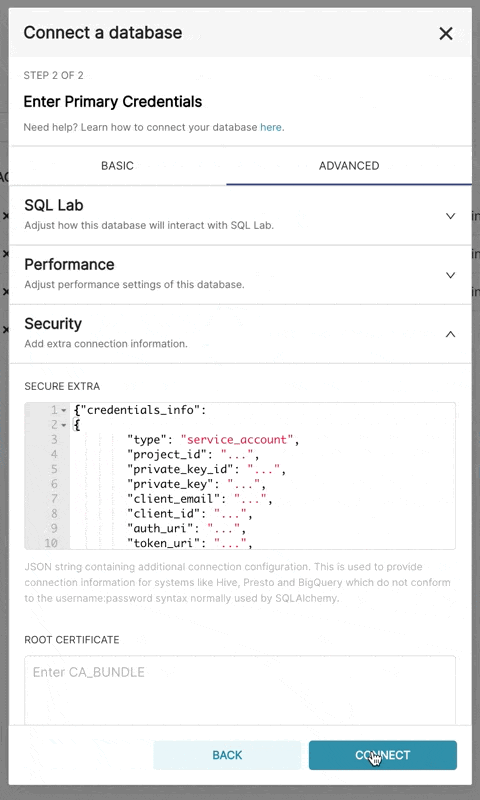
To be able to upload CSV or Excel files to BigQuery in Superset, you'll need to also add the pandas_gbq library.
Currently, the Google BigQuery Python SDK is not compatible with gevent, due to some dynamic monkeypatching on python core library by gevent.
So, when you deploy Superset with gunicorn server, you have to use worker type except gevent.
Additional Resources
Google Sheets
Google Sheets has a very limited SQL API. The recommended connector library for Google Sheets is shillelagh.
There are a few steps involved in connecting Superset to Google Sheets.
Additional Resources
Hana
The recommended connector library is sqlalchemy-hana.
The connection string is formatted as follows:
hana://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}
Apache Hive
The pyhive library is the recommended way to connect to Hive through SQLAlchemy.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
hive://hive@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
Additional Resources
Hologres
Hologres is a real-time interactive analytics service developed by Alibaba Cloud. It is fully compatible with PostgreSQL 11 and integrates seamlessly with the big data ecosystem.
Hologres sample connection parameters:
- User Name: The AccessKey ID of your Alibaba Cloud account.
- Password: The AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account.
- Database Host: The public endpoint of the Hologres instance.
- Database Name: The name of the Hologres database.
- Port: The port number of the Hologres instance.
The connection string looks like:
postgresql+psycopg2://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database}
IBM DB2
The IBM_DB_SA library provides a Python / SQLAlchemy interface to IBM Data Servers.
Here's the recommended connection string:
db2+ibm_db://{username}:{passport}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
There are two DB2 dialect versions implemented in SQLAlchemy. If you are connecting to a DB2 version without LIMIT [n] syntax, the recommended connection string to be able to use the SQL Lab is:
ibm_db_sa://{username}:{passport}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
Apache Impala
The recommended connector library to Apache Impala is impyla.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
impala://{hostname}:{port}/{database}
Kusto
The recommended connector library for Kusto is sqlalchemy-kusto>=2.0.0.
The connection string for Kusto (sql dialect) looks like this:
kustosql+https://{cluster_url}/{database}?azure_ad_client_id={azure_ad_client_id}&azure_ad_client_secret={azure_ad_client_secret}&azure_ad_tenant_id={azure_ad_tenant_id}&msi=False
The connection string for Kusto (kql dialect) looks like this:
kustokql+https://{cluster_url}/{database}?azure_ad_client_id={azure_ad_client_id}&azure_ad_client_secret={azure_ad_client_secret}&azure_ad_tenant_id={azure_ad_tenant_id}&msi=False
Make sure the user has privileges to access and use all required databases/tables/views.
Apache Kylin
The recommended connector library for Apache Kylin is kylinpy.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
kylin://<username>:<password>@<hostname>:<port>/<project>?<param1>=<value1>&<param2>=<value2>
MySQL
The recommended connector library for MySQL is mysqlclient.
Here's the connection string:
mysql://{username}:{password}@{host}/{database}
Host:
- For Localhost:
localhostor127.0.0.1 - Docker running on Linux:
172.18.0.1 - For On Prem: IP address or Host name
- For Docker running in OSX:
docker.for.mac.host.internalPort:3306by default
One problem with mysqlclient is that it will fail to connect to newer MySQL databases using caching_sha2_password for authentication, since the plugin is not included in the client. In this case, you should use mysql-connector-python instead:
mysql+mysqlconnector://{username}:{password}@{host}/{database}
IBM Netezza Performance Server
The nzalchemy library provides a Python / SQLAlchemy interface to IBM Netezza Performance Server (aka Netezza).
Here's the recommended connection string:
netezza+nzpy://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
OceanBase
The sqlalchemy-oceanbase library is the recommended way to connect to OceanBase through SQLAlchemy.
The connection string for OceanBase looks like this:
oceanbase://<User>:<Password>@<Host>:<Port>/<Database>
Ocient DB
The recommended connector library for Ocient is sqlalchemy-ocient.
Install the Ocient Driver
pip install sqlalchemy-ocient
Connecting to Ocient
The format of the Ocient DSN is:
ocient://user:password@[host][:port][/database][?param1=value1&...]
Oracle
The recommended connector library is cx_Oracle.
The connection string is formatted as follows:
oracle://<username>:<password>@<hostname>:<port>
Additional Resources
Parseable
Parseable is a distributed log analytics database that provides SQL-like query interface for log data. The recommended connector library is sqlalchemy-parseable.
The connection string is formatted as follows:
parseable://<username>:<password>@<hostname>:<port>/<stream_name>
For example:
parseable://admin:admin@demo.parseable.com:443/ingress-nginx
Note: The stream_name in the URI represents the Parseable logstream you want to query. You can use both HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443) connections.
Additional Resources
Apache Pinot
The recommended connector library for Apache Pinot is pinotdb.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
pinot+http://<pinot-broker-host>:<pinot-broker-port>/query?controller=http://<pinot-controller-host>:<pinot-controller-port>/``
The expected connection string using username and password is formatted as follows:
pinot://<username>:<password>@<pinot-broker-host>:<pinot-broker-port>/query/sql?controller=http://<pinot-controller-host>:<pinot-controller-port>/verify_ssl=true``
If you want to use explore view or joins, window functions, etc. then enable multi-stage query engine. Add below argument while creating database connection in Advanced -> Other -> ENGINE PARAMETERS
{"connect_args":{"use_multistage_engine":"true"}}
Additional Resources
Postgres
Note that, if you're using docker compose, the Postgres connector library psycopg2 comes out of the box with Superset.
Postgres sample connection parameters:
- User Name: UserName
- Password: DBPassword
- Database Host:
- For Localhost: localhost or 127.0.0.1
- For On Prem: IP address or Host name
- For AWS Endpoint
- Database Name: Database Name
- Port: default 5432
The connection string looks like:
postgresql://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database}
You can require SSL by adding ?sslmode=require at the end:
postgresql://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database}?sslmode=require
You can read about the other SSL modes that Postgres supports in Table 31-1 from this documentation.
More information about PostgreSQL connection options can be found in the SQLAlchemy docs and the PostgreSQL docs.
Additional Resources
QuestDB
QuestDB is a high-performance, open-source time-series database with SQL support. The recommended connector library is the PostgreSQL driver psycopg2, as QuestDB supports the PostgreSQL wire protocol.
The connection string is formatted as follows:
postgresql+psycopg2://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
The default port for QuestDB's PostgreSQL interface is 8812.
Additional Resources
Presto
The pyhive library is the recommended way to connect to Presto through SQLAlchemy.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
presto://{hostname}:{port}/{database}
You can pass in a username and password as well:
presto://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
Here is an example connection string with values:
presto://datascientist:securepassword@presto.example.com:8080/hive
By default Superset assumes the most recent version of Presto is being used when querying the datasource. If you’re using an older version of Presto, you can configure it in the extra parameter:
{
"version": "0.123"
}
SSL Secure extra add json config to extra connection information.
{
"connect_args":
{"protocol": "https",
"requests_kwargs":{"verify":false}
}
}
Additional Resources
RisingWave
The recommended connector library for RisingWave is sqlalchemy-risingwave.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
risingwave://root@{hostname}:{port}/{database}?sslmode=disable
Snowflake
Install Snowflake Driver
Follow the steps here about how to install new database drivers when setting up Superset locally via docker compose.
echo "snowflake-sqlalchemy" >> ./docker/requirements-local.txt
The recommended connector library for Snowflake is snowflake-sqlalchemy.
The connection string for Snowflake looks like this:
snowflake://{user}:{password}@{account}.{region}/{database}?role={role}&warehouse={warehouse}
The schema is not necessary in the connection string, as it is defined per table/query. The role and warehouse can be omitted if defaults are defined for the user, i.e.
snowflake://{user}:{password}@{account}.{region}/{database}
Make sure the user has privileges to access and use all required databases/schemas/tables/views/warehouses, as the Snowflake SQLAlchemy engine does not test for user/role rights during engine creation by default. However, when pressing the “Test Connection” button in the Create or Edit Database dialog, user/role credentials are validated by passing “validate_default_parameters”: True to the connect() method during engine creation. If the user/role is not authorized to access the database, an error is recorded in the Superset logs.
And if you want connect Snowflake with Key Pair Authentication. Please make sure you have the key pair and the public key is registered in Snowflake. To connect Snowflake with Key Pair Authentication, you need to add the following parameters to "SECURE EXTRA" field.
Please note that you need to merge multi-line private key content to one line and insert \n between each line
{
"auth_method": "keypair",
"auth_params": {
"privatekey_body": "-----BEGIN ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----\n...\n...\n-----END ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----",
"privatekey_pass":"Your Private Key Password"
}
}
If your private key is stored on server, you can replace "privatekey_body" with “privatekey_path” in parameter.
{
"auth_method": "keypair",
"auth_params": {
"privatekey_path":"Your Private Key Path",
"privatekey_pass":"Your Private Key Password"
}
}
Additional Resources
Apache Solr
The sqlalchemy-solr library provides a Python / SQLAlchemy interface to Apache Solr.
The connection string for Solr looks like this:
solr://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{server_path}/{collection}[/?use_ssl=true|false]
Apache Spark SQL
The recommended connector library for Apache Spark SQL pyhive.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
hive://hive@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
Additional Resources
Arc
There are two ways to connect Superset to Arc:
1. Arc with Apache Arrow (Recommended)
The recommended connector library for Arc with Apache Arrow support is arc-superset-arrow.
The connection string looks like:
arc+arrow://{api_key}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
2. Arc with JSON
Alternatively, you can use the JSON connector arc-superset-dialect.
The connection string looks like:
arc+json://{api_key}@{hostname}:{port}/{database}
Arc supports multiple databases (schemas) within a single instance. In Superset, each Arc database appears as a schema in the SQL Lab.
Note: The Arrow dialect (arc-superset-arrow) is recommended for production use as it provides 3-5x better performance using Apache Arrow IPC binary format.
SQL Server
The recommended connector library for SQL Server is pymssql.
The connection string for SQL Server looks like this:
mssql+pymssql://<Username>:<Password>@<Host>:<Port-default:1433>/<Database Name>
It is also possible to connect using pyodbc with the parameter odbc_connect
The connection string for SQL Server looks like this:
mssql+pyodbc:///?odbc_connect=Driver%3D%7BODBC+Driver+17+for+SQL+Server%7D%3BServer%3Dtcp%3A%3Cmy_server%3E%2C1433%3BDatabase%3Dmy_database%3BUid%3Dmy_user_name%3BPwd%3Dmy_password%3BEncrypt%3Dyes%3BConnection+Timeout%3D30
You might have noticed that some special charecters are used in the above connection string. For example see the odbc_connect parameter. The value is Driver%3D%7BODBC+Driver+17+for+SQL+Server%7D%3B which is a URL-encoded form of Driver={ODBC+Driver+17+for+SQL+Server};. It's important to give the connection string is URL encoded.
For more information about this check the sqlalchemy documentation. Which says When constructing a fully formed URL string to pass to create_engine(), special characters such as those that may be used in the user and password need to be URL encoded to be parsed correctly. This includes the @ sign.
SingleStore
The recommended connector library for SingleStore is sqlalchemy-singlestoredb.
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
singlestoredb://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database}
StarRocks
The sqlalchemy-starrocks library is the recommended way to connect to StarRocks through SQLAlchemy.
You'll need to the following setting values to form the connection string:
- User: User Name
- Password: DBPassword
- Host: StarRocks FE Host
- Catalog: Catalog Name
- Database: Database Name
- Port: StarRocks FE port
Here's what the connection string looks like:
starrocks://<User>:<Password>@<Host>:<Port>/<Catalog>.<Database>
Additional Resources
TDengine
TDengine is a High-Performance, Scalable Time-Series Database for Industrial IoT and provides SQL-like query interface.
The recommended connector library for TDengine is taospy and taos-ws-py
The expected connection string is formatted as follows:
taosws://<user>:<password>@<host>:<port>
For example:
taosws://root:taosdata@127.0.0.1:6041
Teradata
The recommended connector library is teradatasqlalchemy.
The connection string for Teradata looks like this:
teradatasql://{user}:{password}@{host}
ODBC Driver
There's also an older connector named sqlalchemy-teradata that requires the installation of ODBC drivers. The Teradata ODBC Drivers are available here: https://downloads.teradata.com/download/connectivity/odbc-driver/linux
Here are the required environment variables:
export ODBCINI=/.../teradata/client/ODBC_64/odbc.ini
export ODBCINST=/.../teradata/client/ODBC_64/odbcinst.ini
We recommend using the first library because of the lack of requirement around ODBC drivers and because it's more regularly updated.
TimescaleDB
TimescaleDB is the open-source relational database for time-series and analytics to build powerful data-intensive applications. TimescaleDB is a PostgreSQL extension, and you can use the standard PostgreSQL connector library, psycopg2, to connect to the database.
If you're using docker compose, psycopg2 comes out of the box with Superset.
TimescaleDB sample connection parameters:
- User Name: User
- Password: Password
- Database Host:
- For Localhost: localhost or 127.0.0.1
- For On Prem: IP address or Host name
- For Timescale Cloud service: Host name
- For Managed Service for TimescaleDB service: Host name
- Database Name: Database Name
- Port: default 5432 or Port number of the service
The connection string looks like:
postgresql://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database name}
You can require SSL by adding ?sslmode=require at the end (e.g. in case you use Timescale Cloud):
postgresql://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database name}?sslmode=require
Additional Resources
Trino
Supported trino version 352 and higher
Connection String
The connection string format is as follows:
trino://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{catalog}
If you are running Trino with docker on local machine, please use the following connection URL
trino://trino@host.docker.internal:8080
Authentications
1. Basic Authentication
You can provide username/password in the connection string or in the Secure Extra field at Advanced / Security
-
In Connection String
trino://{username}:{password}@{hostname}:{port}/{catalog} -
In
Secure Extrafield{
"auth_method": "basic",
"auth_params": {
"username": "<username>",
"password": "<password>"
}
}
NOTE: if both are provided, Secure Extra always takes higher priority.
2. Kerberos Authentication
In Secure Extra field, config as following example:
{
"auth_method": "kerberos",
"auth_params": {
"service_name": "superset",
"config": "/path/to/krb5.config",
...
}
}
All fields in auth_params are passed directly to the KerberosAuthentication class.
NOTE: Kerberos authentication requires installing the trino-python-client locally with either the all or kerberos optional features, i.e., installing trino[all] or trino[kerberos] respectively.
3. Certificate Authentication
In Secure Extra field, config as following example:
{
"auth_method": "certificate",
"auth_params": {
"cert": "/path/to/cert.pem",
"key": "/path/to/key.pem"
}
}
All fields in auth_params are passed directly to the CertificateAuthentication class.
4. JWT Authentication
Config auth_method and provide token in Secure Extra field
{
"auth_method": "jwt",
"auth_params": {
"token": "<your-jwt-token>"
}
}
5. Custom Authentication
To use custom authentication, first you need to add it into
ALLOWED_EXTRA_AUTHENTICATIONS allow list in Superset config file:
from your.module import AuthClass
from another.extra import auth_method
ALLOWED_EXTRA_AUTHENTICATIONS: Dict[str, Dict[str, Callable[..., Any]]] = {
"trino": {
"custom_auth": AuthClass,
"another_auth_method": auth_method,
},
}
Then in Secure Extra field:
{
"auth_method": "custom_auth",
"auth_params": {
...
}
}
You can also use custom authentication by providing reference to your trino.auth.Authentication class
or factory function (which returns an Authentication instance) to auth_method.
All fields in auth_params are passed directly to your class/function.
Additional Resources
Vertica
The recommended connector library is sqlalchemy-vertica-python. The Vertica connection parameters are:
- User Name: UserName
- Password: DBPassword
- Database Host:
- For Localhost : localhost or 127.0.0.1
- For On Prem : IP address or Host name
- For Cloud: IP Address or Host Name
- Database Name: Database Name
- Port: default 5433
The connection string is formatted as follows:
vertica+vertica_python://{username}:{password}@{host}/{database}
Other parameters:
- Load Balancer - Backup Host
YDB
The recommended connector library for YDB is ydb-sqlalchemy.
Connection String
The connection string for YDB looks like this:
ydb://{host}:{port}/{database_name}
Protocol
You can specify protocol in the Secure Extra field at Advanced / Security:
{
"protocol": "grpcs"
}
Default is grpc.
Authentication Methods
Static Credentials
To use Static Credentials you should provide username/password in the Secure Extra field at Advanced / Security:
{
"credentials": {
"username": "...",
"password": "..."
}
}
Access Token Credentials
To use Access Token Credentials you should provide token in the Secure Extra field at Advanced / Security:
{
"credentials": {
"token": "...",
}
}
Service Account Credentials
To use Service Account Credentials, you should provide service_account_json in the Secure Extra field at Advanced / Security:
{
"credentials": {
"service_account_json": {
"id": "...",
"service_account_id": "...",
"created_at": "...",
"key_algorithm": "...",
"public_key": "...",
"private_key": "..."
}
}
}
YugabyteDB
YugabyteDB is a distributed SQL database built on top of PostgreSQL.
Note that, if you're using docker compose, the Postgres connector library psycopg2 comes out of the box with Superset.
The connection string looks like:
postgresql://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database}
Additional Resources
Connecting through the UI
Here is the documentation on how to leverage the new DB Connection UI. This will provide admins the ability to enhance the UX for users who want to connect to new databases.
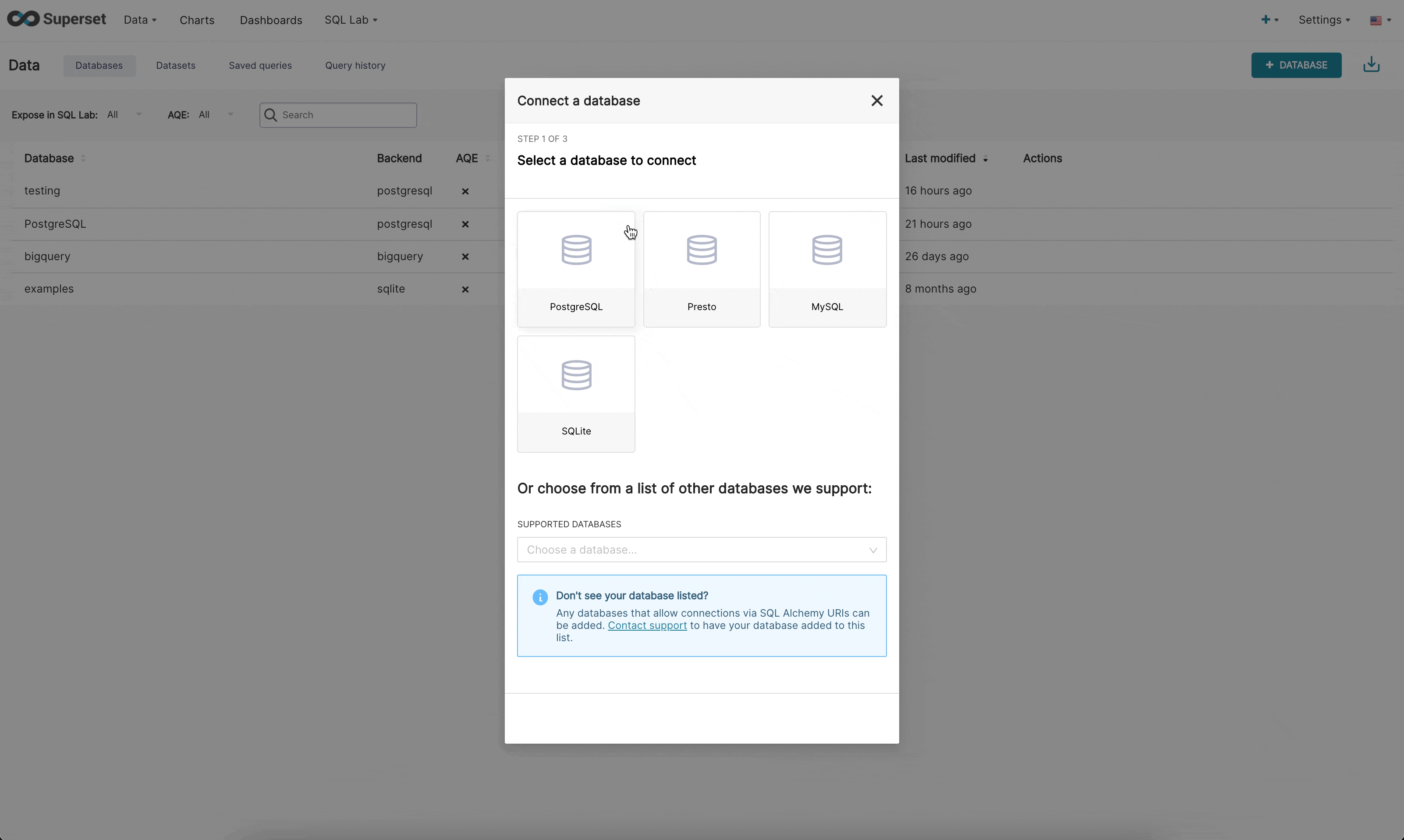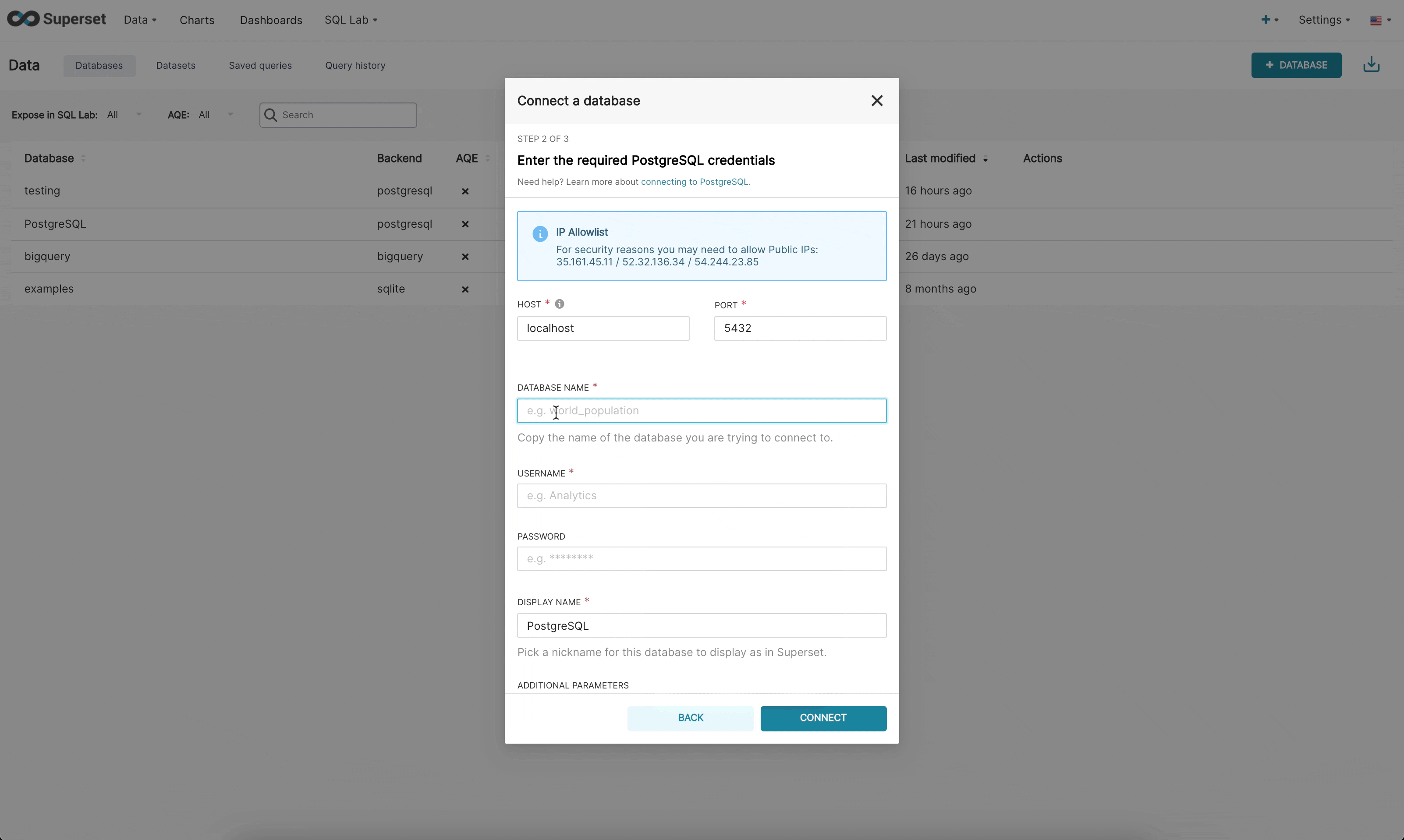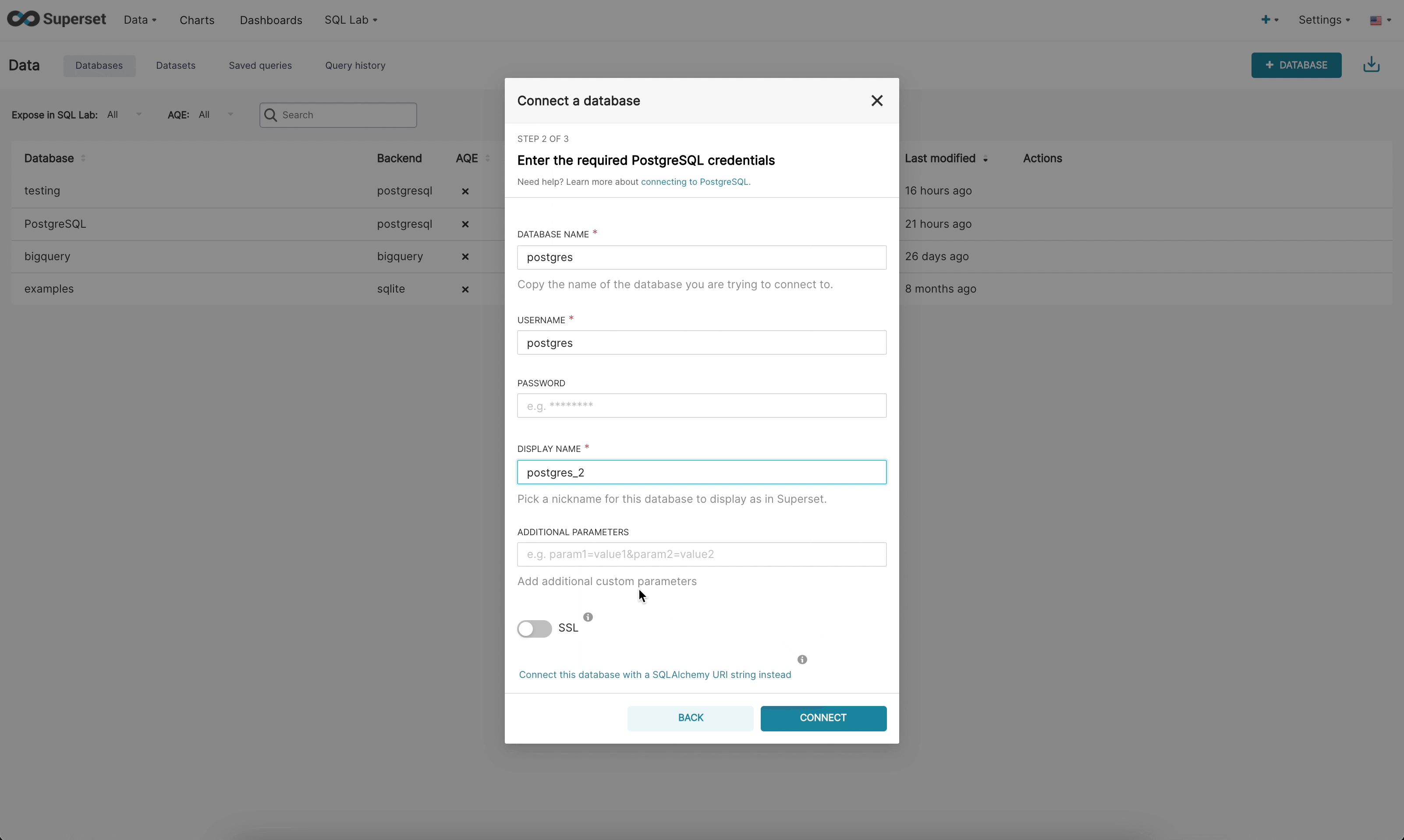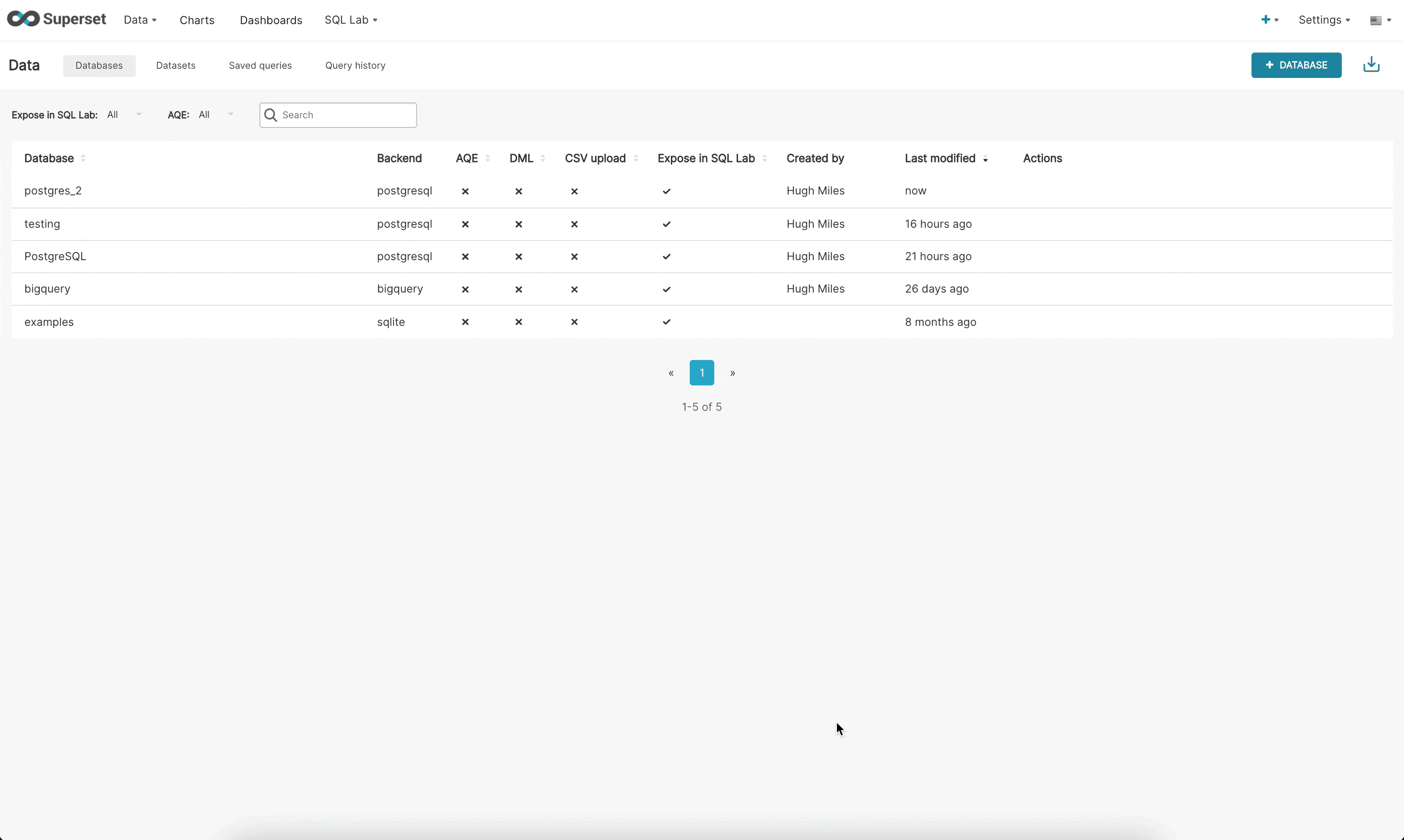
There are now 3 steps when connecting to a database in the new UI:
Step 1: First the admin must inform superset what engine they want to connect to. This page is powered by the /available endpoint which pulls on the engines currently installed in your environment, so that only supported databases are shown.
Step 2: Next, the admin is prompted to enter database specific parameters. Depending on whether there is a dynamic form available for that specific engine, the admin will either see the new custom form or the legacy SQLAlchemy form. We currently have built dynamic forms for (Redshift, MySQL, Postgres, and BigQuery). The new form prompts the user for the parameters needed to connect (for example, username, password, host, port, etc.) and provides immediate feedback on errors.
Step 3: Finally, once the admin has connected to their DB using the dynamic form they have the opportunity to update any optional advanced settings.
We hope this feature will help eliminate a huge bottleneck for users to get into the application and start crafting datasets.
How to setup up preferred database options and images
We added a new configuration option where the admin can define their preferred databases, in order:
# A list of preferred databases, in order. These databases will be
# displayed prominently in the "Add Database" dialog. You should
# use the "engine_name" attribute of the corresponding DB engine spec
# in `superset/db_engine_specs/`.
PREFERRED_DATABASES: list[str] = [
"PostgreSQL",
"Presto",
"MySQL",
"SQLite",
]
For copyright reasons the logos for each database are not distributed with Superset.
Setting images
- To set the images of your preferred database, admins must create a mapping in the
superset_text.ymlfile with engine and location of the image. The image can be host locally inside your static/file directory or online (e.g. S3)
DB_IMAGES:
postgresql: "path/to/image/postgres.jpg"
bigquery: "path/to/s3bucket/bigquery.jpg"
snowflake: "path/to/image/snowflake.jpg"
How to add new database engines to available endpoint
Currently the new modal supports the following databases:
- Postgres
- Redshift
- MySQL
- BigQuery
When the user selects a database not in this list they will see the old dialog asking for the SQLAlchemy URI. New databases can be added gradually to the new flow. In order to support the rich configuration a DB engine spec needs to have the following attributes:
parameters_schema: a Marshmallow schema defining the parameters needed to configure the database. For Postgres this includes username, password, host, port, etc. (see).default_driver: the name of the recommended driver for the DB engine spec. Many SQLAlchemy dialects support multiple drivers, but usually one is the official recommendation. For Postgres we use "psycopg2".sqlalchemy_uri_placeholder: a string that helps the user in case they want to type the URI directly.encryption_parameters: parameters used to build the URI when the user opts for an encrypted connection. For Postgres this is{"sslmode": "require"}.
In addition, the DB engine spec must implement these class methods:
build_sqlalchemy_uri(cls, parameters, encrypted_extra): this method receives the distinct parameters and builds the URI from them.get_parameters_from_uri(cls, uri, encrypted_extra): this method does the opposite, extracting the parameters from a given URI.validate_parameters(cls, parameters): this method is used foronBlurvalidation of the form. It should return a list ofSupersetErrorindicating which parameters are missing, and which parameters are definitely incorrect (example).
For databases like MySQL and Postgres that use the standard format of engine+driver://user:password@host:port/dbname all you need to do is add the BasicParametersMixin to the DB engine spec, and then define the parameters 2-4 (parameters_schema is already present in the mixin).
For other databases you need to implement these methods yourself. The BigQuery DB engine spec is a good example of how to do that.
Extra Database Settings
Deeper SQLAlchemy Integration
It is possible to tweak the database connection information using the parameters exposed by SQLAlchemy. In the Database edit view, you can edit the Extra field as a JSON blob.
This JSON string contains extra configuration elements. The engine_params object gets unpacked
into the sqlalchemy.create_engine call, while the metadata_params get unpacked into the
sqlalchemy.MetaData call. Refer to the SQLAlchemy docs for more information.
Schemas
Databases like Postgres and Redshift use the schema as the logical entity on top of the database. For Superset to connect to a specific schema, you can set the schema parameter in the Edit Tables form (Sources > Tables > Edit record).
External Password Store for SQLAlchemy Connections
Superset can be configured to use an external store for database passwords. This is useful if you a running a custom secret distribution framework and do not wish to store secrets in Superset’s meta database.
Example: Write a function that takes a single argument of type sqla.engine.url and returns the
password for the given connection string. Then set SQLALCHEMY_CUSTOM_PASSWORD_STORE in your config
file to point to that function.
def example_lookup_password(url):
secret = <<get password from external framework>>
return 'secret'
SQLALCHEMY_CUSTOM_PASSWORD_STORE = example_lookup_password
A common pattern is to use environment variables to make secrets available.
SQLALCHEMY_CUSTOM_PASSWORD_STORE can also be used for that purpose.
def example_password_as_env_var(url):
# assuming the uri looks like
# mysql://localhost?superset_user:{SUPERSET_PASSWORD}
return url.password.format(**os.environ)
SQLALCHEMY_CUSTOM_PASSWORD_STORE = example_password_as_env_var
SSL Access to Databases
You can use the Extra field in the Edit Databases form to configure SSL:
{
"metadata_params": {},
"engine_params": {
"connect_args":{
"sslmode":"require",
"sslrootcert": "/path/to/my/pem"
}
}
}
Custom Error Messages
You can use the CUSTOM_DATABASE_ERRORS in the superset/custom_database_errors.py file or overwrite it in your config file to configure custom error messages for database exceptions.
This feature lets you transform raw database errors into user-friendly messages, optionally including documentation links and hiding default error codes.
Provide an empty string as the first value to keep the original error message. This way, you can add just a link to the documentation Example usage:
CUSTOM_DATABASE_ERRORS = {
"database_name": {
re.compile('permission denied for view'): (
__(
'Permission denied'
),
SupersetErrorType.GENERIC_DB_ENGINE_ERROR,
{
"custom_doc_links": [
{
"url": "https://example.com/docs/1",
"label": "Check documentation"
},
],
"show_issue_info": False,
}
)
},
"examples": {
re.compile(r'message="(?P<message>[^"]*)"'): (
__(
'Unexpected error: "%(message)s"'
),
SupersetErrorType.GENERIC_DB_ENGINE_ERROR,
{}
)
}
}
Options:
custom_doc_links: List of documentation links to display with the error.show_issue_info: Set toFalseto hide default error codes.
Misc
Querying across databases
Superset offers an experimental feature for querying across different databases. This is done via a special database called "Superset meta database" that uses the "superset://" SQLAlchemy URI. When using the database it's possible to query any table in any of the configured databases using the following syntax:
SELECT * FROM "database name.[[catalog.].schema].table name";
For example:
SELECT * FROM "examples.birth_names";
Spaces are allowed, but periods in the names must be replaced by %2E. Eg:
SELECT * FROM "Superset meta database.examples%2Ebirth_names";
The query above returns the same rows as SELECT * FROM "examples.birth_names", and also shows that the meta database can query tables from any table — even itself!
Considerations
Before enabling this feature, there are a few considerations that you should have in mind. First, the meta database enforces permissions on the queried tables, so users should only have access via the database to tables that they originally have access to. Nevertheless, the meta database is a new surface for potential attacks, and bugs could allow users to see data they should not.
Second, there are performance considerations. The meta database will push any filtering, sorting, and limiting to the underlying databases, but any aggregations and joins will happen in memory in the process running the query. Because of this, it's recommended to run the database in async mode, so queries are executed in Celery workers, instead of the web workers. Additionally, it's possible to specify a hard limit on how many rows are returned from the underlying databases.
Enabling the meta database
To enable the Superset meta database, first you need to set the ENABLE_SUPERSET_META_DB feature flag to true. Then, add a new database of type "Superset meta database" with the SQLAlchemy URI "superset://".
If you enable DML in the meta database users will be able to run DML queries on underlying databases as long as DML is also enabled in them. This allows users to run queries that move data across databases.
Second, you might want to change the value of SUPERSET_META_DB_LIMIT. The default value is 1000, and defines how many are read from each database before any aggregations and joins are executed. You can also set this value None if you only have small tables.
Additionally, you might want to restrict the databases to with the meta database has access to. This can be done in the database configuration, under "Advanced" -> "Other" -> "ENGINE PARAMETERS" and adding:
{"allowed_dbs":["Google Sheets","examples"]}